Giraffes in the East African savannas adapt well to warmer temperatures. However, they are threatened by increasingly heavy rainfall.
Climate change is expected to cause widespread declines in wildlife populations worldwide. Climate anomalies interacting with human pressures can place additional stress on already declining populations, but little is known about the interactions between climate and anthropogenic effects on large African herbivore species despite the growing importance of these pressures. Giraffes are endangered megaherbivores, but the combined climate and human effects on the survival rates not only of giraffes, but of any large African herbivore species, had not been studied. We concluded a decade-long study – the largest to date – of a giraffe population in the Tarangire region of Tanzania. The study area spanned more than a thousand square kilometers, including areas inside and outside protected areas. Contrary to expectations, higher temperatures were found to positively affect adult giraffe survival, while rainier wet seasons negatively impacted adult and calf survival. The results were published in the journal Biodiversity and Conservation.
First exploration into the effects of climate variation on giraffe survival
Our research team quantified the effects of local anomalies of temperature, rainfall, and vegetation greenness on the probability of survival of the giraffes. We also explored whether climate had a greater effect on giraffes that were also experiencing human impacts at the edges of the protected reserves.
Studying the effects of climate and human pressures on a long-lived and slow-breeding animal like a giraffe requires monitoring their populations over a lengthy time period and over a large area, enough to capture both climate variation and any immediate or delayed effects on survival. We obtained nearly two decades of data on local rainfall, vegetation greenness, and temperature during Tanzania’s short rains, long rains, and dry season, and then followed the fates of 2,385 individually recognized giraffes of all ages and sexes over the final 8 years of the two-decade period.

Surprising effects of temperature on giraffe survival
We had predicted that higher temperatures would hurt adult giraffes because their very large body size might make them overheat, but higher temperatures positively affected adult giraffe survival. This is because the giraffe has several physical features that help it to keep cool, like long necks and legs for evaporative heat loss, specialized nasal cavities, an intricate network of arteries that supply blood to the brain, and they radiate heat through their spot patches. However, temperatures during our study period may not have exceeded the tolerable thermal range for giraffes, and an extreme heat wave in the future might reveal a threshold above which these massive animals might be harmed. So we will continue to monitor this population.
Heavy rains may increase parasites while reducing nutritional value of vegetation
Survival of giraffe adults and calves was reduced during rainier wet seasons, which we attributed to a possible increase in parasites and disease. A previous study in the Tarangire region showed giraffe gastrointestinal parasite intensity was higher during the rainy seasons than the dry season, and heavy flooding has caused severe outbreaks of diseases known to cause mortality in giraffes, such as Rift Valley Fever Virus and anthrax. The current study also found higher vegetation greenness reduced adult giraffe survival, potentially because faster leaf growth reduces nutrient quality in giraffe food.
Human pressure place additional stress on already declining populations
Climate effects were exacerbated by the giraffe’s proximity to the edge of protected reserves, but not during every season. Our findings indicate that giraffes living near the peripheries of the protected areas are most vulnerable during heavy short rains. These conditions likely heighten disease risks associated with livestock, and muddy terrain hampers anti-poaching patrols, leading to increased threats to giraffe survival.
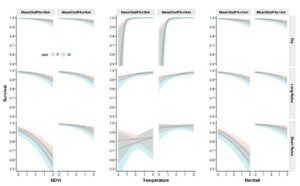
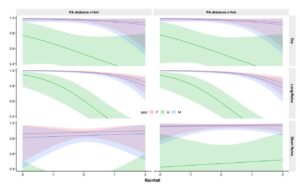
We concluded that projected climate changes in East Africa, including heavier rainfall during the short rains, will likely threaten persistence of giraffes in one of Earth’s most important landscapes for large mammals, indicating the need for effective land-use planning and anti-poaching to improve giraffes’ resilience to the coming changes.
The paper is available for download at https://doi.org/10.1007/s10531-023-02645-4